The Future of Medicine: A Glimpse of What’s to Come
In the world of medicine, we’ve seen incredible advancements over the centuries, but a recent discovery takes us one step closer to a futuristic solution for diabetes treatment. Imagine a medicine so small, only a few thousand atoms in size, yet incredibly dynamic. This medicine isn’t just a passive agent; it adapts, changes shape, and responds to the body’s needs in real-time. This breakthrough is being hailed as a revolutionary step in the ongoing fight against diabetes, offering the potential for self-aware treatments that react to the body’s fluctuating glucose levels without the need for constant monitoring.
A Brief History of Medicine’s Battle with Diabetes
Medicine 1.0: Ancient Beginnings
Diabetes, one of the oldest documented diseases, was first described in 1550 BCE in ancient Egypt. Physicians at the time noted symptoms like excessive urination and prescribed herbal remedies, which were largely ineffective. By 400 BCE, Indian physicians observed that ants were attracted to the urine of individuals with diabetes due to its sweetness. They categorized diabetes into two types:
- A rapid, fatal form (later identified as Type 1 Diabetes).
- A slower, less severe form (later identified as Type 2 Diabetes).

Medicine 2.0: Observation and Empiricism
During the Renaissance, observations of diabetes became more sophisticated. European physicians confirmed the sweetness of diabetic urine and began associating the condition with the pancreas and diet. For centuries, however, treatment remained primitive, often involving starvation diets that were unsustainable and ineffective.
Medicine 3.0: The Discovery of Insulin
The true revolution began in 1921 when Frederick Banting and Charles Best extracted insulin from a cow pancreas and tested it on diabetic dogs. The results were miraculous: the treatment reversed diabetes symptoms almost instantly.

Challenges of Insulin Therapy
While insulin was a breakthrough, it wasn’t perfect. Patients needed to:
- Monitor blood sugar levels multiple times daily.
- Administer precise insulin doses, often through injections.
These challenges turned diabetes management into a full-time job for many patients. This raised an important question: Could there be a smarter, more adaptive solution?
Medicine 4.0: Smarter Solutions for Diabetes
The Search for Self-Aware Medicine
The latest development in diabetes treatment takes a huge leap forward: self-aware medicine. Rather than relying on patients to monitor and adjust their insulin, this new medicine would automatically respond to changes in glucose levels, much like how the body’s natural insulin production works. It’s as if the medicine itself “senses” glucose levels and adjusts accordingly, eliminating the need for constant intervention.
The Science Behind Synthetic Lectins
The biggest challenge in creating glucose-responsive medicine lies in the similarities between glucose and other substances like fructose and sucrose. These substances are chemically similar, which could lead to the medicine mistakenly reacting to the wrong molecules. However, researchers at the University of Bristol managed to overcome these challenges by developing synthetic lectins—artificial proteins that bind specifically to glucose and release it when necessary.
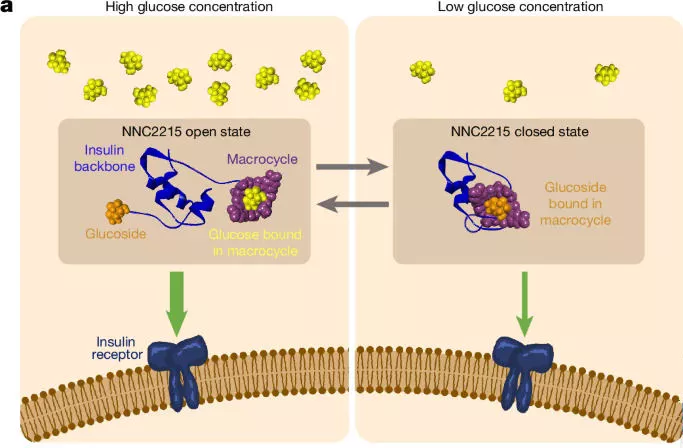
Turning the Idea into Reality
Taking this discovery from the lab to the real world required significant effort. In 2018, the team behind this breakthrough teamed up with Novo Nordisk, one of the largest producers of insulin, to scale up the research. This collaboration helped the team move forward with their project, eventually resulting in the creation of a molecule that could bind glucose and release it under the right conditions. By attaching a glucose-binding molecule to insulin, they created a compound that would only release insulin when glucose levels rise, reducing the risk of administering the wrong dose at the wrong time. Learn more about Novo Nordisk.
Overcoming Challenges
A PhD student named Harry, inspired by the potential of synthetic lectins, launched a startup to advance this technology. Harry’s team faced significant challenges:
- Limited lab space and resources.
- Early candidates were promising but required refinement to achieve real-world efficiency.
Despite these hurdles, the team succeeded in creating a system that binds and releases glucose more effectively than both biological and synthetic alternatives.

The Road Ahead: A New Era in Diabetes Treatment
With these advancements, we may soon see a world where diabetes patients no longer need to manually inject insulin or monitor their glucose levels continuously. Instead, the medicine would do it all for them. While this breakthrough is still in the early stages, the potential it holds is monumental, marking the beginning of medicine 4.0: a future where treatments are highly personalized and self-adjusting.
What Does Medicine 4.0 Mean for the Future of Healthcare?
Medicine 4.0 is not just about diabetes. It represents the broader shift toward personalized, adaptive treatments that can address complex diseases with minimal patient intervention. This new era of medicine has the potential to transform healthcare as we know it.
Related Resources:
- Learn more about the history of insulin discovery.
- Explore the University of Bristol’s research on synthetic lectins.
- Understand the science behind nanomedicine.
Medicine 4.0 isn’t a distant dream. It’s a reality being built today. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, we’re not just treating diseases—we’re reimagining what it means to be healthy.

best blog